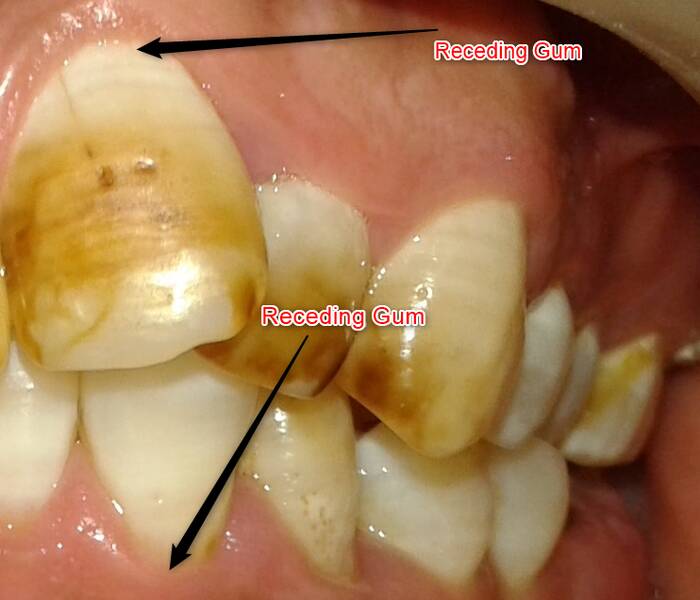
Is gum recession reversible? What are the possible causes of gum recession? How can I recognize the symptoms of gum recession? What is the best treatment for gum recession? And finally, how can a gingival recession be prevented?
I. What Is Gingival Recession?
Gingival recession, or gingival retraction, is the manifestation of a gradual retreat of the gums in the mouth.
Gum recession leaves the teeth bare and exposed to bacteria. It can easily lead to tooth loosening in the long run.
II. Is Gum Recession Reversible?
In the current state of health care, it is not possible to really cure gum recession. Once it is noticed, it is important to consult your dentist.
The causes of dental recession are many and varied. But unfortunately, once the gum tissue is reduced, it is impossible to push it back in.
Once you’ve noticed your gum recession and seen your doctor, he or she will first look for the cause of your problem.
Even if it is impossible to rebuild the tissue, once the cause is determined, your dentist can find a way to at least stop the process.
In the case of dental disease or pathology, it will have to be treated first, to be sure to slow down or stop the gum loss.
And if the loss is too great, there are solutions to help you. But although there are ways to improve your condition, gum recession is not reversible.
III. Potential Causes of Gum Recession
1. Periodontitis
When bacteria have grown in the gums, especially from untreated tartar, the gums can lose tissue and cause gum recession.
2. Bruxism (Teeth Grinding)
Bruxism is also called teeth grinding. If you have bruxism, you may grind your teeth at night while you sleep. Over time, bruxism can cause your gums to recede.
3. Aggressive Brushing
If you brush your teeth too hard and with a hard toothbrush, you can injure your gums. Constantly assaulting the gum tissue can cause it to recede.
4. Poor Oral Hygiene
When plaque builds up, it can turn into tartar if not properly treated. Irregular or overly aggressive tooth brushing can cause gum recession.
5. Chewing Tobacco
Chewing tobacco allows nicotine to enter the mouth directly into the bloodstream.
Nicotine is a poison.
Gum loss in chewers is even greater than in smokers.
6. Perforations and Piercings
Piercings and other cosmetic perforations made on the gum are a risk of infection. Teeth close to the piercing are at risk of infection, and the risk of gingival recession is great.
7. Hormonal Influence (Teenager, Pregnancy…)
The production of hormones that accompany puberty or during pregnancy is one of the natural causes of gum problems.
8. Genetics (Thin Gum Tissue)
There is an undeniable hereditary factor that plays a role in dental pathologies. Some people are simply born with weaker gum tissue.
Their risk of developing gum recession is greater.
9. Some Orthodontic Treatments
Gum recession can also be caused by orthodontic treatment. For example, braces can cause gum recession because they rub against the gums.
10. Dental Malocclusion
Teeth that are misaligned when the gums are closed can cause gum recession. This is why it is important to consult early on in case of dental malocclusion.
11. Aging
As with other parts of the body, the tissues of the mouth are not spared from aging. It is not uncommon with time and age to develop gum recession.
12. Diabetes
When you have diabetes, an inflammation of the blood vessels around the gum is possible.
Because of this, the gums are not irrigated enough and various periodontal diseases can affect them.
IV. Symptoms of Gingival Recession
1. Gum Bleeding
Gum bleeding is one of the main symptoms of gum recession.
It is common to have gum bleeding when brushing your teeth. This is one of the most common signs.
2. Long Teeth
When you feel that your teeth are longer, as if they have grown, then you should be concerned.
This feeling of long teeth is due to the fact that with gum retraction, your teeth appear longer because they are more exposed.
3. Redness and Pain of the Gum
Redness and pain in the gums are signs of gum disease. They often appear when the gums are infected, and can eventually lead to gum recession.
4. Bad Breath
Bad breath can accompany gum recession. It can be caused by cavities or periodontitis.
It is therefore quite common to have bad breath when you have gum recession.
5. Spacing of the Teeth
If you have teeth that are a little too far apart, it may be a sign of gum recession.
Tooth spacing is a common symptom that should not be taken lightly. Loss of gum tissue can make tooth spacing worse.
6. Hypersensitivity of the Teeth and Gums
Because the gums protect the teeth, when you start to lose gum tissue the gum protection drops.
The direct cause is therefore pain and hypersensitivity of the teeth and gums.
7. Abnormal Tooth Mobility
In the long run, gum recession can lead to abnormal tooth mobility and even tooth loosening.
When the gums lose strength and recede, the teeth are less supported by the tissue and can move on their own.
V. Treatment of Gum Recession (Gum Grafting)
Surgery may be necessary in cases of severe gum recession. If the gum tissue is too small, then your dentist may decide to perform gum surgery.
This is a gum graft. The tissue is taken from the palate or nearby healthy gum tissue and inserted into the area where the gum is receding.
VI. How to Prevent Gum Recession?
1. Choose a softer toothbrush
Gum recession is irreversible. For this reason, it is best to take preventive action to avoid gum recession.
Brush your teeth with a soft toothbrush that won’t hurt your gums while cleaning your teeth.
2. Scaling at the Dentist
It is important to have your teeth scaled from time to time at your dentist. Your dentist will be able to remove even the tartar that is present on the teeth under the gums.
This will prevent gingivitis in the long run and keep you away from the risk of gum retraction.
3. Treatment of Bruxism
If you suffer from bruxism, seek treatment and consult your dentist. Antidepressants can be prescribed, as well as dental protectors.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking is extremely harmful to the health of your teeth, so it is necessary to quit smoking to give your mouth a chance to heal.
5. See your Dentist Regularly
Even if you don’t like to visit your dentist, it is necessary to do so at least twice a year. Regular visits will keep you away from various oral diseases.
VII. Other Questions About Gingival Recession
1. Is There any Natural Treatment for Gum Recession?
As a natural treatment for gum recession, you can massage your gums with a mixture of coconut oil and Himalayan pink salt.
You can also rub aloe vera gel on your gums or even drink it.
2. How Much Does a Gum Graft Cost?
The cost of a gum graft can vary from one area to another and from one doctor to another and is usually between $500 and $1400 per tooth. So if you treat more than 4 teeth you can go up to $4000.
Periodontists are dentists who specialize in this type of gum-related problem.
There is an additional charge if the replacement tissue comes from another donor and is not taken from your mouth for any medical reason.
3. Why Does the Gum Recede?
There are several reasons for gum retraction. Periodontitis, as well as gingivitis, and certain diseases such as diabetes or age, are all causes of gum retraction.
4. Which Mouthwash for Periodontitis?
Mouthwashes have been specially designed to fight against periodontitis. These mouthwashes are antiseptic.
This type of mouthwash is not to be used daily. You can make a mouthwash with bicarbonate.
Useful Links:
Etiology and occurrence of gingival recession
Prevalence of gingival recession and study of associated related factors in young UK adults
Current status of periodontal disease in adults
Swollen salivary glands [Infection, Causes & Treatments]
How Do You Release a Closed Locked Jaw (Trismus)?