How do I get rid of a mucous cyst in my mouth? What to do about a mucous cyst in the mouth? Is it dangerous? Is there a risk of cancer? How to get rid of it permanently? And finally, what are the natural remedies to relieve the pain of mucoceles?
I. What Is Mucous Cysts?
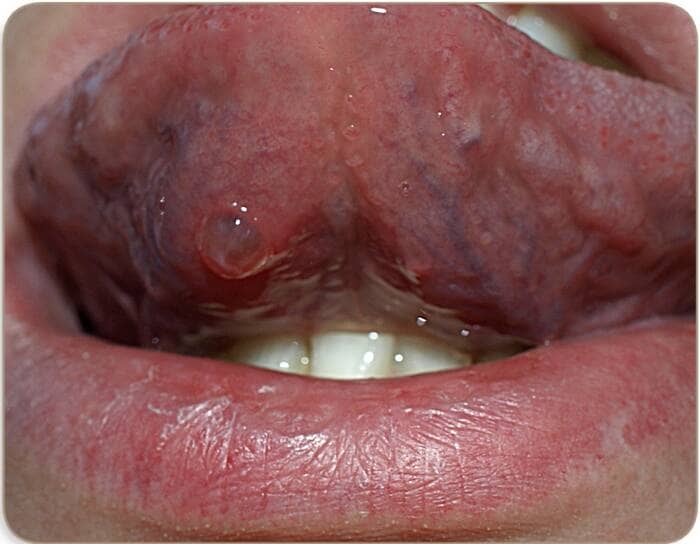
Mucous cysts are also known as mucoceles. These lesions are usually located in the inner labial area and affect the accessory salivary glands.
These lesions can be of two types.
The first type represents mucous cysts that appear as a result of a rupture of the gland’s epithelium. This causes spillage and accumulation of saliva into the intraglandular space; hence the formation of the cyst. This is called extravasation mucocele.
The second type of mucous cyst is a retention cyst. In this case, saliva is blocked due to an epithelial proliferation in the excretory duct.
The lower lip is the area where mucous cysts develop in 60 to 80% of cases.
Normally, these lesions are asymptomatic and do not cause any pain. However, they may not only be numerous, but recurrent, and may cause severe pain.
The cause of mucous cysts is blocked accessory salivary glands.
The accessory salivary glands are salivary glands, but tiny in size, scattered throughout the mouth.
II. How Do I Get Rid of a Mucous Cyst in My Mouth?
The usual treatment for mucous cysts is a surgical operation: surgical removal of the mucocele. This operation is done under local anesthesia.
Before performing this surgical removal, an additional examination can be done to confirm the diagnosis that it is a mucous cyst.
This is the orthopantomogram.
This examination can reveal salivary lithiasis and rule out other options.
An incision is made in the area of the cyst. The nodule is then removed with a blade scalpel. Constant visual control is required to avoid severing a nerve branch.
Discontinuous sutures without tension are used to close the incision.
The operation to get rid of a mucous cyst usually does not leave a scar.
After the operation, swelling or bruising may be visible. Usually, painkillers and mouthwash are prescribed to facilitate healing.
Healing takes 2 to 8 weeks, with no visible after-effects.
III. Natural Treatments to Relieve a Mucous Cyst
1. Honey to Soothe Mucous Cyst
Make a paste with a teaspoon of raw honey and ¼ of a spoon of turmeric. Place the mixture on the mucocele and leave it on for 15-20 minutes.
After this time, gargle with warm water. For more effect, apply honey to the affected area before going to bed.
This tip should be repeated 2 to 3 times a day until the symptoms improve.
You can also simply put Manuka honey on your mucous cyst as often as possible.
Honey has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
2. Ice to Calm Mucous Cysts
You can use ice to numb the area affected by the cyst and thus get some relief.
Simply place ice cubes in a washcloth and apply it against your skin for a minute.
Sipping cold water as you pass by is also a way to ease the pain associated with the mucous cyst.
3. Glycerin for Mucous Cysts
To use glycerin on your mucocele, you need to dab some on the affected area.
There is no time limit, it can stay on as long as you want. Once the glycerin pad is removed, rinse your mouth with cold water.
Do this 3 to 4 times a day.
A glycerin-based mouthwash can also give you great relief. Use it several times a day.
Because it is antiseptic and healing, glycerin is an easy way to get rid of a mucocele.
IV. Is There Any Risk of Cancer?
A mucous cyst or mucocele is usually a non-cancerous tumor. This means that although it has arisen because of a change in the cells, they are not metastatic.
Nevertheless, there are cases where the appearance of a mucous cyst can be a sign of a tumor process.
These are called appendicular tumors, which can be of two types: epithelial or non-epithelial (often neuroendocrine).
This is why we recommend that you visit your dentist at least twice a year, who will probably refer you to the right specialist, depending on your pathology.
Useful Links:
Mucous Cyst: A Clinical-Surgical Study
Dermatologic Manifestations of Mucocele (Mucous Cyst) Workup
Mucous Cyst (Mucocele)A Clinicopathologic and Histochemical Study