How do I get rid of fungus on my gums? What is gum fungus? How long does gum fungus last? Gum Fungus that doesn’t go away. What to do? What is the link between gum fungus and smoking? And what foods should I avoid if I have gum fungus? What to eat in case of fungus on the gum? And finally, what are the links with fungal infections of the throat and tongue?
I. What Is Gum Fungus?
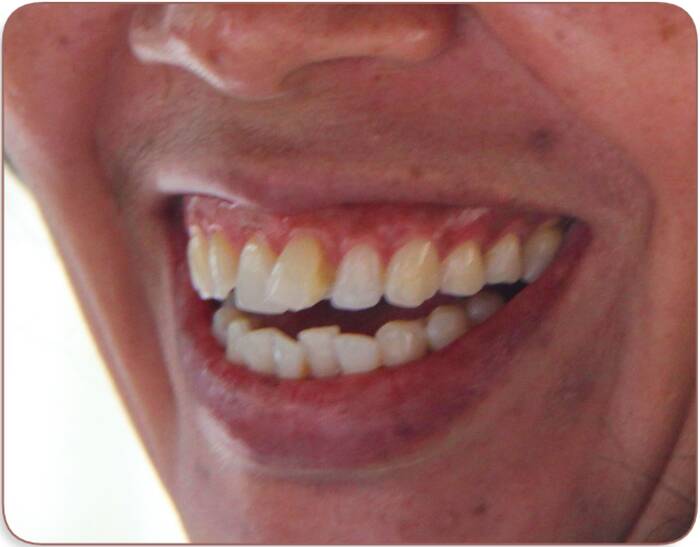
Gum fungus is often associated with oral candidiasis. The common point between the two pathologies is that they are caused by a fungus.
In the case of gum disease, the fungus attacks this part of the body and causes bad breath or loose teeth. Since it weakens the gums, they can no longer play their role.
It should be noted that mycosis or candidiasis is not a contagious disease that is transmitted by an infected person.
It is rather a consequence of an imbalance of micro-organisms that are naturally present in the mouth.
II. What Are the Symptoms of Fungus on the Gum
Gum fungus usually occurs after taking a medication that has upset the bacterial balance in your mouth.
It also happens if you have been sick if you have undergone heavy treatment or when you wear braces and do not follow the rules of hygiene.
What are the signs that you have gum fungus?
The first thing that should alert you is when you feel discomfort during meals.
Also, if you notice small white spots on your gums, it may be a fungus.
Especially if you notice other signs such as red, black, or green patches, lesions at the corner of the mouth, and bad breath.
III. How Do I Get Rid of Fungus on my Gums?
# Natural Treatment
For fungus on the gum, some natural treatments can be of great help. They can considerably reduce the risk of aggravation of the disease.
- Baking soda is generally used to whiten teeth. In the case of a fungus on the gum, you just need to put a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth.
- Caprylic acid is found in palm oil and coconut oil. It has antifungal and antimicrobial properties against fungal infections.
- Propolis helps fight fungus and stimulate the immune system.
- Raw or cooked garlic can be taken as a dietary supplement.
- Essential oils of laurel, tea tree, cinnamon, and oregano are also useful, especially against Candida Albicans.
# Medical Treatment
If you notice the symptoms, it is important to consult a dentist quickly. He will use a probe that he will push into the diseased area to check the level of inflammation.
The doctor may prescribe tablets to be sucked several times a day. He or she may also prescribe a solution to keep in the mouth for a few minutes two or three times a day or a gel.
These are antifungal treatments that are quick and very effective on the fungus of the mouth and therefore of the gums.
He can also prescribe antiseptic mouthwashes or essential oils based on laurel.
IV. How Long Does Gum Fungus Last?
If you notice the first symptoms of oral fungus, it is important to visit a doctor, preferably a dentist.
A simple examination of the mouth is usually all that is needed for a diagnosis. With proper treatment and if you follow the doctor’s recommendations to the letter, the duration of an oral fungus, including gums, is between one and three weeks.
After fighting the infection, it is possible to avoid a recurrence. The best way is to have good oral hygiene.
As a reminder, you should brush your teeth twice a day with a soft brush and fluoride toothpaste. You should also floss and visit a dentist regularly.
V. Gum Fungus that Does Not Go Away. What to Do?
As a rule, if a person uses natural remedies to fight oral fungus and adopts good dental hygiene, he or she will have satisfactory results within a few days.
However, if you have used these grandmother remedies and have not found satisfaction or even over-the-counter treatments, you should consult a dentist and explain in detail the natural treatments you have used.
After an examination, he can prescribe more effective medical treatments. And in some cases, apart from gels and sucking tablets, they can perform a scaling.
VI. Gum Fungus and Tobacco
As you probably already know, tobacco is the cause of many mouth infections such as fungal infections.
Indeed, tobacco can be the cause of periodontal disease that affects the gums. It is characterized by redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums that are caused by an accumulation of bacteria.
Although gingivitis also affects non-smokers due to poor dental and oral hygiene, it is important to know that the chemical and toxic substances contained in tobacco increase the risk of contracting the infection.
If this infection is not taken care of quickly, the consequences can be serious.
The bacteria attack the gums and bones that hold the teeth in place. And once the teeth are no longer supported, you lose them.
Once you stop smoking, you greatly reduce the risk of gum disease.
VII. Foods to Avoid in Case of Fungus on the Gum
If you have a fungus in your mouth or oral infection, it is important to pay attention to your diet, especially during treatment.
You should not eat sugars that promote the growth of fungi. You should also avoid fermented foods or foods that contain yeast such as bread or cheese.
Of course, as far as beverages are concerned, you must avoid all soda, or alcoholic beverages such as beer, wine, etc.
In addition, all dairy products or lactose such as yogurt for example. Also, do not take any acidic products, excitants like tea, coffee, alcohol, and of course cigarettes.
If you have to avoid these foods during the treatment, you should limit their consumption at least six months later.
VIII. What to Eat in Case of Fungus on the Gum
Apart from all the foods mentioned above, you are allowed to eat anything that gives you pleasure.
Whether it is meat, fish, chicken, vegetables… But you must be careful with the seasoning. Not too salty, not too spicy.
IX. What Are the Links Between Mycosis of the Throat and Mycosis of the Tongue?
There is a link between mycosis of the throat and mycosis of the tongue. However, it must be kept in mind that a mycosis is not a transmissible disease between organs.
So it cannot be transmitted from the tongue to the throat.
However, the fungus can reach the mucous membranes of the throat and make the lymph nodes that are located around the throat sensitive.
This is why oral or tongue fungus is often accompanied by discomfort in your throat. Especially during swallowing.
Useful Links:
The oral fungal mycobiome: characteristics and relation to periodontitis in a pilot study
New antimicrobial therapies used against fungi present in subgingival sites
Oral Fungal Infections: Past, Present, and Future
How to stop excess saliva at night? [Medical & Home Remedies]
Can rheumatoid arthritis affect your teeth? [causes & Symptoms]