Swollen salivary glands and Infection, what to do? Treatments? Causes? What is a dry mouth (Xerostomia)? Sialadenitis? What are the different diseases of the salivary glands that can cause swelling? And finally what are the natural solutions for swollen salivary glands?
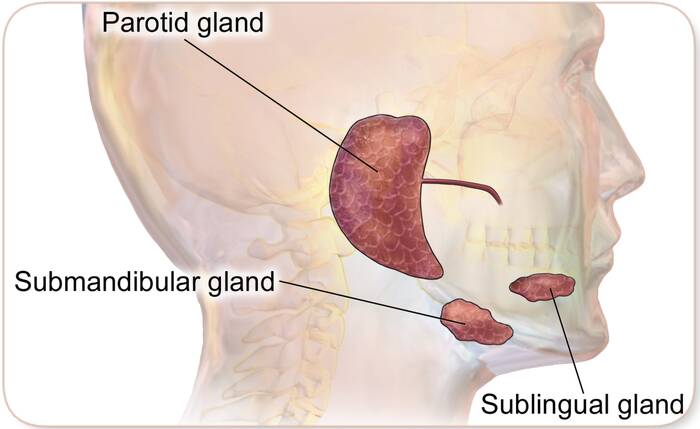
I. What Are Salivary Glands?
1. Parotid Glands
The parotid glands are among the main salivary glands. The parotid gland is the largest of all the salivary glands, and there is one on each side of the face.
Each parotid gland has two lobes, each on one side of the facial nerve.
2. Submaxillary Glands
As the name suggests, the submaxillary glands are located under the jaw. These glands are smaller than the parotid glands.
There are two submaxillary glands, each located under the chin and tongue, at the back of the lower jaw.
3. Sublingual Glands
Of all the major salivary glands, the sublingual gland is the smallest. As with the other salivary glands, there are two sublingual glands.
It is through these glands that the saliva enters the mouth through innumerable sublingual ducts. The sublingual glands are under the floor of the mouth, deeply buried on each side of the tongue.
II. What Is Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)?
Xerostomia is the scientific name for dry mouth. A dry mouth is a fact of having an insufficient production of saliva in the mouth.
Since saliva plays an important role in the health of teeth, dry mouth is an oral risk.
Symptoms of xerostomia include a pasty mouth, bad breath, and chapped lips.
III. Different Diseases of the Salivary glands (Causes)
1. Bacterial Infections of the Salivary glands
One of the main diseases that can affect the salivary glands is a bacterial infection.
This can develop if there is an obstacle in the mouth to the discharge of saliva. This obstacle can be a narrowing of the canal for example.
When saliva gets stuck in the gland, an infection is possible. You may then have swollen, painful parotid glands and even a fever.
2. Viral infections of the Salivary Glands
The salivary glands are not immune to viruses. One of the most dangerous viruses for the salivary glands is the mumps virus, called paramyxovirus or “mumps” virus.
Signs of mumps include ear and throat pain, swollen glands, and fever.
Mumps can cause complications, especially in teenagers, pregnant women, and adults.
3. Salivary Gland Stones (Lithiasis)
Stones can form under the submaxillary glands.
These stones prevent the normal flow of saliva, which can cause a painless swelling of the gland.
Lithiasis is normally an inconsequential pathology of the salivary gland.
4. Swelling of the Salivary Glands
Swollen salivary glands can have several causes. You may notice that the lower part of your mouth is swollen, or the angle of your jaw.
It is also possible that this swelling is painful, or on the contrary to have swollen parotid glands without pain.
Swollen salivary glands can be the result of an infection, a virus, or even a tumor.
5. Painless Enlargement of the Salivary Glands
In the case of painless enlargement of the salivary glands, the swelling is often the result of a disease.
Liver disease, diabetes, anorexia, or alcoholism can all be the cause.
6. Spasms and Stenosis
Other elements can affect the salivary glands. Spasms and stenosis can indeed cause a blockage of the salivary glands, with more or less serious consequences.
Saliva that stagnates in the sublingual canals can cause an infection of the salivary glands.
7. Salivary Gland Tumors
Two types of tumors can affect the salivary glands: benign and malignant.
In the case of benign tumors, it is often the parotid glands that are affected. The nodule is isolated and mobile and grows slowly.
Malignant tumors are cancers of the salivary glands. In this case, the nodule is hard and immobile, because it is part of the adjacent tissue.
8. Sjögren’s Syndrome
Sjögren’s syndrome is a pathology that mainly affects women over 40 years of age. It results in the production of antibodies that eventually attack the lacrimal and salivary glands.
Dry eyes and mouth are usually signs of Sjögren’s syndrome. But the diagnosis can only be made by your doctor after your blood has been tested and the presence of these antibodies has been found.
9. Pseudo-Allergic Sialitis
The diagnosis of pseudo-allergic sialitis is still difficult to make, because the causes of this pathology remain, to this day, unknown.
Pseudo-allergic sialitis manifests itself by a swelling of the glands which can be painful, during meals or when the senses of taste and smell are stimulated.
This swelling may be accompanied by pruritus.
IV. Swollen Salivary Glands, what Are Treatments?
1. Bacterial Infections of the Salivary Glands
In the case of swollen glands due to a bacterial infection, it is important to consult a doctor.
Antibiotic treatment will be prescribed. In addition to this, the evolution of the disease and the healing will be followed by an ultrasound control.
2. Cases of Viral Infections of the Salivary Glands
Remedies for swollen salivary glands in case of viral infection do not contain antibiotics. Antibiotics are only necessary if the virus causes a bacterial superinfection.
Because the ears usually heal on their own, treatment for a viral infection of the salivary glands mainly treats the fever and pain.
For this, you may be prescribed painkillers and antipyretics.
3. Salivary Gland Stones (Lithiasis)
Regular massage of the gland will help to get rid of the stones. If this is not enough, your doctor may consider a sialendoscopy.
This is an endoscopy of the salivary ducts and glands. Extracorporeal shock waves can also be used to destroy stones;
This technique is called extracorporeal lithotripsy.
4) Painless Enlargement of the Salivary Glands
If you have painless salivary gland enlargement, treatment will depend largely on the condition that is causing your glands to swell.
Your doctor will be able to help you identify the cause (diabetes, alcoholism…) and the treatment will be based on that cause.
5. Cases of Salivary Gland Tumors
Salivary gland tumors are treated differently if they are benign or malignant. Benign tumors are treated by surgical removal. Malignant tumors are treated either by surgery or by radiation therapy.
The treatment of salivary gland cancer depends on its evolution. Sometimes it may be necessary to remove lymph nodes in the neck.
6. Sjögren’s Syndrome
Sjögren’s syndrome is not treatable as such, but there are ways to manage the various symptoms.
Taking immunosuppressants, such as eye drops, helps reduce eye symptoms.
Saliva stimulants can also be used to combat dry mouth.
Because Sjögren’s syndrome is an immune system disorder, immunosuppressants can be used to address the signs of this condition.
7. Cases of Pseudo-Allergic Sialitis
Treatment for pseudo-allergic sialitis includes a 2-week course of dual antibiotics, anti-allergic drugs and benzodiazepine, corticosteroids, and antispasmodics. In the long term, treatment includes weak corticosteroids and antiallergics.
V. Natural Solutions for Swollen Salivary Glands
To act in case of swollen salivary glands, you can start by drinking plenty of water, to which you will have added lemon juice.
The acidity of the lemon juice can increase salivary production, necessary for oral health.
In case of painful glands, apply warm compresses to the swelling to relieve you.
If your swelling is due to stones, then take vitamin supplements like magnesium.
You can also take a spoonful of turmeric mixed with almond milk twice a day.
VI. Other Issues Concerning Swollen Salivary Glands
1. What Are the Signs of Salivary Gland Cancer?
Difficulty swallowing, a lump in the mouth, or stiffness of the facial muscles are all signs of salivary gland cancer.
It is also possible to develop trismus, a difficulty to open wide the mouth. Pain is present in cancer, especially in the mouth, jaw, throat, and neck.
2. Which Doctor Treats Swollen Salivary Glands?
The stomatologist is a health professional who specializes in problems related to the mouth and jaw. He or she is the one who deals with health problems related to the salivary glands.
Stomatology is a branch of maxillofacial surgery.
3. Are the Salivary Glands Palpable?
If you have any doubts about the health of your salivary glands, it is possible to palpate the glands during your medical examination. The doctor can do this with the submandibular glands or the parotid glands.
It is even possible to massage the glands when they are swollen, to reduce the swelling.
4. Is Parotitis Contagious?
Parotitis caused by mumps is very contagious. Mumps parotitis can be spread by coughing, sneezing, or by close contact with people who are sick.
If you have never had mumps, you can be infected if you are around someone who is sick.
That’s why it’s important to get the mumps vaccine, MMR (Measles-Mumps-Rubella).
5. What Are the Signs of Mumps?
The symptoms of mumps are fever and temperature. There is also a painful swelling of the parotid glands behind the jaw.
Other signs of mumps include earache, headache, fatigue, difficulty chewing, or loss of appetite.
It is important to note that mumps may be asymptomatic at the onset of infection, while the carrier is contagious.
Useful Links:
Salivary Gland diseases causes
How Do I Get Rid of a Mucous Cyst in my Mouth?
White Spot on Gums and Mouth with no Pain, What to Do?
Why Won’t My Canker Sore Go Away?
I Have Really Bad Teeth what Are My Options?
Can rheumatoid arthritis affect your teeth? [causes & Symptoms]