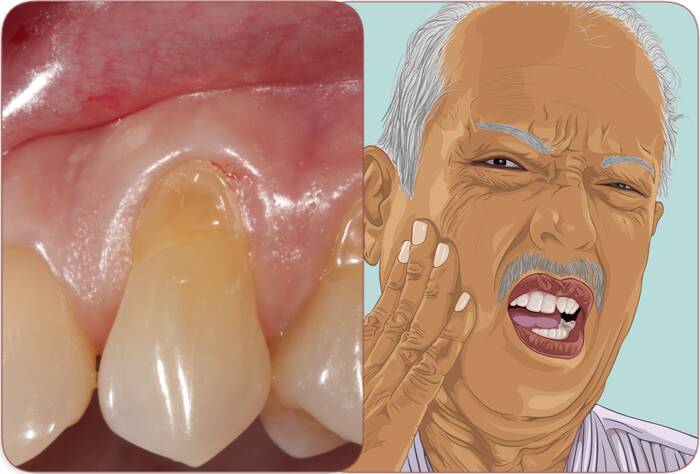
How do you treat inflamed and irritated gums? What are the different causes of irritated gums? How can they be prevented? What are the two stages of evolution of irritated gums? Where does gum pain come from? And finally, how to treat gum inflammation?
I. Causes of Inflamed and Irritated Gums
There are several causes of irritated gums. First, you may have gingivitis, a gum disease caused by excess plaque.
Periodontitis can also be the cause of a gum problem.
It is also common to develop gum irritation if you have bad lifestyle habits, such as smoking.
Poor oral hygiene can also irritate your gums.
II. How Do You Treat Inflamed and Irritated Gums
1. Simple Scaling for Gingivitis
One of the first symptoms of gingivitis is bleeding gums. If you bleed regularly while brushing, you may have gingivitis.
In this case, scaling is necessary. Scaling removes plaque from your teeth.
Once this is done, all you have to do is follow the rules of hygiene to cure your gingivitis.
2. Deep Scaling for Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a kind of gingivitis that has evolved. To get rid of periodontitis, simple scaling is not effective enough.
Your dentist must do a thorough scaling. To do this, root planing is added to the traditional scaling, which allows the removal of plaque everywhere in the mouth, including under the teeth and on the gums.
3. Surgery for Severe Cases
Sometimes surgery may be necessary for periodontitis. This is the case if the gums have been too badly damaged.
It is then necessary to reconstitute a part of the gums so that the teeth can hold firmly onto it.
Periodontitis can evolve without the patient’s knowledge, and once at the practitioner’s office, the latter can discover that the bone is largely destroyed by the infection.
III. Inflamed and Irritated Gums, how to Prevent Them?
1. Improve Your Brushing
Irritated gums are partly due to poor dental hygiene. To prevent gum problems, start by brushing your teeth at least twice a day, especially before bedtime.
Avoid hard toothbrushes that can irritate your gums. Brush both the teeth and the gum line carefully, separating the teeth from the gums.
2. Rinse Your Mouth Regularly
Mouthwash is a good way to prevent gingivitis. It helps eliminate bacteria that may remain in the mouth after brushing.
It is also an excellent way to fight bad breath.
So remember to make mouthwash part of your routine, if not every day, at least with some regularity.
3. Anti-Gingivitis Toothpaste
There are toothpastes specially designed to fight gingivitis. These kinds of toothpaste are often composed of baking soda or triclosan.
They are effective in balancing the oral flora and fighting against bacterial proliferation.
By incorporating an anti-gingivitis toothpaste into your oral hygiene routine, you reduce the risk of developing gum irritation.
4. Avoid Eating Sugar
Eating sugar, especially refined sugar, is dangerous to your dental health. Not only can sugar weaken your teeth and put you at risk for cavities.
Sugar can also lodge on your teeth or gums, causing plaque. To avoid gingivitis, it’s best to reduce your sugar intake.
5. Paying Attention to Your Diet
It is important to watch what you eat if you want to maintain good oral hygiene.
Sugary products such as sodas or sweets are dangerous for your teeth.
This is also the case with ice cream, citrus fruits, or tomatoes.
Be careful with these foods if you want to protect your gums.
6. Flossing
Flossing can help get rid of food residue that can’t be removed by brushing.
Make a habit of flossing after each brushing. These food scraps, if not removed, will become clumps of bacteria that will cause severe damage to your mouth.
IV. The Two Stages of an Irritated Gum
1. Gingivitis:
Gingivitis is the first stage of gum disease. Its symptoms are red gums and bleeding during brushing.
Gingivitis is related to the proliferation of tartar on the teeth, which has become plaque.
It is the bacteria that have started to attack the gums that cause these symptoms.
2. Periodontitis:
When gingivitis is poorly treated or not treated at all, it can degenerate into periodontitis.
Periodontitis is a much more serious infection, which means that the plaque has spread. In the case of periodontitis, the tissues are affected by bacteria.
The risk of tooth decay is high and the treatment is more difficult.
V. Where Does Gum Pain Come from?
Gum pain can have several origins. More frequently, you may have gum pain because of bacteria that have developed there.
This can be due to gingivitis, an abscess, or a canker sore.
VI. How to Relieve Pain and Treat Gum Inflammation Naturally?
To relieve gum pain, you can use homeopathy. There are also natural oils that can help you.
For example, you can make a natural mouthwash by mixing 15 ml of honey with 3 to 5 drops of Roman chamomile EO.
Another natural tip is to chew propolis gum or mallow leaf.
VII. Other Questions About Inflamed and Irritated Gums
1. How to Heal a Hole in the Gum?
To help your gum heal, you can opt for a natural saltwater mouthwash. This is usually recommended by dentists after tooth extraction.
All you have to do is mix a teaspoon of salt with a glass of water. Use this solution to rinse your mouth.
2. What Is the Best Mouthwash for Gums?
It is difficult to find the best mouthwash for gums. All the major toothpaste brands have produced mouthwashes suitable for gum problems.
You can turn to Eludril mouthwash or Parodontal fresh mint. But there are many others.
3. What Are the Symptoms of Gum Cancer?
The first sign of gum cancer is pain. This pain occurs both during chewing and swallowing and is permanent.
Apart from this symptom, gum cancer is manifested by gingival bleeding and tooth loosening.
4. How to Wash the Mouth with Baking Soda?
Mouthwash with baking soda is easy to make. All you need to do is mix a teaspoon of baking soda with a glass of water. With this product, you can rinse your mouth as often as necessary.
But baking soda can also be used directly as toothpaste. Dampen your toothbrush, tap it in baking soda and brush your teeth and gums with it.
5. How to Treat a Gum Abscess?
Gum abscesses must be drained. The appearance of a dental abscess is not to be taken lightly. It is best to have your abscess drained by a dentist.
It may be necessary to clean the infected tissue and even remove a tooth.
However, you can take action before your dental appointment and relieve the pain with paracetamol. Avoid anti-inflammatory drugs, which can make the pain worse.
Use mouthwash twice a day.
Use anaesthetic gel on the painful area, or place a clove on it.
Useful Links:
An oral health optimized diet can reduce gingival and periodontal inflammation in humans